Authors: José María Jorquera Valero, UMU and Pedro Miguel Sánchez Sánchez, UMU
This blog article is a lightweight excerpt of D4.1: Design of Zero Touch Service Management with Security & Trust Solutions published in January 2021.
The deployment of 5G networks and the development of beyond 5G technologies offer advanced technical capabilities that are enabling the emergence of new services which are principally centered on network stakeholders, such as trading computing resources (i.e., selling or renting), or segmenting and distributing the resources in between different domains. In this context, the automated creation and management of the services, with minimal human intervention, also known as zero-touch management [ETSI-ZSM], has become an essential requirement to ensure the proper functioning of these services, enabling real-time responses to possible incidents or scalability needs.
Yet, as the resources that form a 5G-enabled service are based on logically segmented and geographically distributed virtualized infrastructures, zero-touch management demands new solutions capable of accurately controlling these network resources into an end-to-end service with identical performance as whether resources were physically deployed within the stakeholder’s domain.
In addition, along with the growth of the 5G network, its performance and the number of services offered, new security risks appear in a complex threat landscape for beyond 5G networks [Lourenco-20]. Hence, new security threats (and in a higher number) need to be covered, both internal to a given domain and also regarding the required communication between resources deployed in different domains.
5G networks and beyond also introduce new pervasive and scalable approaches, which tend to contemplate distributed approaches rather than the centralised ones envisaged in previous networks (i.e., 3G and 4G). In this sense, distributed approaches have promoted collaboration between different service/resource consumers and providers, who may or may not have trust links among them. This is a critical aspect that may regulate whether a business transaction is successful or not. Nonetheless, trust is something subjective, based on previous information and experiences among stakeholders, including indirect relationships. Thus, trust management becomes very complex in environments with numerous entities involved, requiring new solutions in this area that are adapted to the relationships underpinned by 5G services [Kumar-18].
Security and trust solutions need to be integrated with the lifecycle management of the network environment. However, due to the already mentioned distributed nature of the 5G services, the service and resource management processes will also require several changes. These changes bring the need for modern slice and service management solutions, enabled by AI-based automation.
Owing to the fact that several pivotal challenges still need to evolve in order to cover the aforementioned capabilities, the 5GZORRO project, and in particular its WP4, leverages the latest technologies to offer the following needs (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: Principal 5GZORRO WP4 mechanisms and services
Security and Trust Orchestration
In a multi-domain and multi-stakeholder scenario, Security and Trust Orchestration are complex and modular tasks because of the number of aspects to be covered, ranging from the internal security deployment for each domain, the trust evaluation of the different stakeholders, the security of the communications among different domains, and lastly, the need for ensuring security when certain critical workloads go across different tenants and different stakeholders.
For these reasons, the 5GZORRO security and trust component is divided into various modules according to their scope (see red boxes of Figure 2). In particular, these modules are:
- Trust Management Framework, which manages the computation of trust values among different stakeholders based on previous experiences and the trust chain with other intermediary entities involved in the trust link. By means of this framework, end-to-end trustworthiness relationships can be established.
- Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) Security Management, which orchestrates the triggering of Trusted Execution Environments for secure computation of critical tasks, assuring security, reliability and privacy-preserving to the actions deployed within this environment.
- Intra-domain security at the business level, which is in charge of detecting and mitigating possible vulnerabilities and attacks inside the network of each stakeholder, enhancing internal security for resources and services.
- Inter-domain security establishment at the communication level, which manages the establishment of secure and trusted connections between different domains in the 5GZORRO environment, guaranteeing privacy and integrity properties without sacrificing performance. The inter-domain module’s objectives are in turn supported by the Identity and permissions management module that supplies mechanisms required for identifying, authenticating and authorising all 5GZORRO entities.
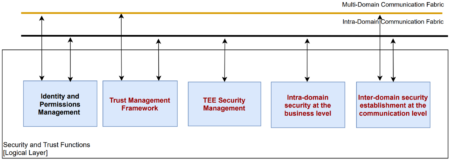
Figure 2. Security and Trust modules contemplated in the WP4 of 5GZORRO
In the end, these modules act as the tools providing the needed security and trust functionalities to the intra- and inter-domain orchestration and management components existing in the 5GZORRO platform. Hence, security and trust orchestration come into play as an enabler for the proper platform functioning, guaranteeing high reliability in its functioning.
Intelligent and Automated Slice & Service Management
Zero-touch automatization and AI for networks play a key role in the 5G evolution and beyond 5G networks. Hence, intelligent and automated management solutions are still required in order to build cross-domain slices and services in distributed multi-stakeholders 5G ecosystems, as mentioned earlier.
By following the direction, the 5GZORRO Intelligent and Automated Slice and Service Manager (ISSM) module is focused on the automation of managing secure cross-domain slices and services within them. The focus is on how to implement intelligent and automated slice and service management in distributed multi-party 5G scenarios through a policy-based protection approach, whose mechanisms will make it possible to control and preserve data confidentiality, integrity and availability features in information sharing operations.
ISSM is responsible for enforcing business transactions both at the system level by interacting with 5GZORRO MANO and Slicing extensions and with alternative slicing technologies, as well as by managing business transaction context across the entire 5GZORRO platform allowing a principled, repeatable, auditable, and trustworthy interaction among the multiple components of the platform to realize a specific business flow. Note that ISSM is covered by the red box called Intelligent Network Slice Management (see Figure 3).
ISSM is also responsible for the optimization of resource allocation to inter-domain slices subject to SLAs and cost-efficiency targets and its principal functionalities are divided into three main components:
- ISSM Workflow Manager (ISSM-WFM): executes orchestration workflows in a context of a business transaction, such as extending a slice across a second domain in cooperation with the Network Slice and Service Orchestration.
- ISSM Optimizer (ISSM-O): optimizes cost-efficiency trade-off of network services and slices required to be created in a context of a specific business transaction and continuously optimizes services and slices that have been already set up in previous transaction flow executions.
- ISSM MEC Manager (ISSM-MEC): facilitates declarative cloud-native style of managing applications executing in a MEC environment while collaboratively managing MEC infrastructure and MEC services at the host and system levels based on the intents communicated by an application control plane.
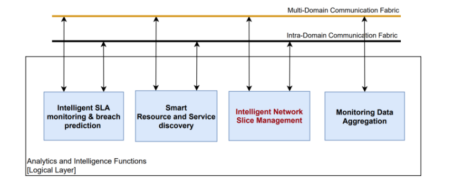
Figure 3. Intelligent and Automated Slice and Service Management module contemplated in WP4
MANO and Slicing Enhancements
In order to provide all the services offered by 5GZORRO, it is essential to develop a set of enhancements for the NFV-MANO and network slicing features to enable required security and trust along with full automation, and thus give support to end-to-end intelligent and secured automated management solutions for services and network slices.
Thus, once considered the background MANO stacks available by the partners (e.g., ETSI OSM, 5GTANGO/SONATA MANO, etc.), a series of NFV-MANO extensions are designed and developed with the objective of keeping control of token-based VNF licensing schemes being part of end-to-end trusted network service chains.
In this sense, both extensions for supporting cloud-native container-based virtual infrastructure managers and harmonizing networking across different platforms are designed and implemented. In particular, these components are:
- Virtual Resource Manager (VRM): is a module in the 5GZORRO platform that directly interacts with the underlying 5G Virtualized platform. Due to its positioning in the 5GZORRO architecture, the VRM offers the upper layers a set of services related to the resources monitoring and management that also includes a direct support to the 5GZORRO Offering Catalogue.
- Network Slice and Service Orchestration (NSSO): is responsible for the automated lifecycle management of the Network Slice (NS) Instances supporting vertical services. This module acts both at the inter-domain and the intra-domain layer of the 5GZORRO architecture. At the inter-domain layer, this module manages the lifecycle of the end-to-end NS mapped to the service, and the split of this end-to-end slice into NS and Network slice subnets (NSS) which will be provisioned by the different domains. At the intra-domain layer, this triggers the lifecycle management actions of the NS and NSS to be provisioned completely intra-domain, interacting with the Virtual Resource Manager for the provisioning of the resources.
- Network Service Mesh Manager (NSMM): provides the functionalities required for the stitching of slice and service across multiple domains. The virtualization platforms the services and slices rely on can be heterogeneous (e.g., VM, Containers) with the aim of providing a true end-to-end multidomain slicing and service context, agnostic with respect to the underlying virtualization technologies.
- e-Licensing Management: encloses a set of tools to bring service providers and software vendors the capabilities to interact in a transparent, flexible and secure way. Both stakeholders will be part of the 5GZORRO ecosystem, trading with the software products with a minimum human intervention, where the software vendors play the role of xNF providers and service providers as xNF consumers.
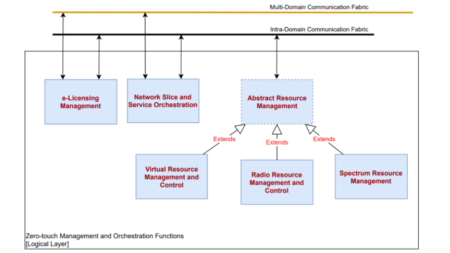
Figure 4. MANO and Slicing modules contemplated in the WP4 of 5GZORRO
References
[Deliverable 4.1 -20] 5GZORRO Consortium (2020). D4.1: Design of Zero Touch Service Management with Security & Trust Solutions. URL: https://www.5gzorro.eu/deliverables/
[ETSI-ZSM] ETSI ZSM ISG information. URL: https://portal.etsi.org/zsm Accessed 27 July 2021.
[Lourenco-20] Lourenco, Marco & Marinos, Louis. (2020). ENISA THREAT LANDSCAPE FOR 5G NETWORKS. DOI: 10.2824/802229
[Kumar-18] Kumar, T., Liyanage, M., Ahmad, I., Braeken, A., & Ylianttila, M. (2018). User privacy, identity and trust in 5G. A Comprehensive Guide to 5G Security, 267-279.
Follow our updates on www.5gzorro.eu.



